Introduction
2020 was a busy year for cyber-security with 3,950 confirmed data breaches. Varonis and the Ponemon Institute calculated the global average cost of a data breach to be $3.86 million – rising to $4.24 million in 2021. It is apparent that many companies are struggling to develop sufficiently robust systems that protect from cyber-security attacks. For small to medium organisations (SMEs) in regulated industries, this may not be a surprise, as dedicating resources towards preventing these data breaches may be considered a lower business decision priority due to budget constraints and the calculated focus of growth.
Our recent blog post on personally identifiable information (PII) built an understanding of sensitive data, the importance of PII in identifying a person’s identity and the expectations of privacy regulations in protecting PII data. The second article in this series explored how Serverless Cloud technologies can help achieve privacy regulation compliance and discussed how organisations can implement tools that aid tracking access, along with protecting and retaining data.
In this article, we will look at the common elements of a data breach plan, as well as discuss key tips you can use to create a robust and well-maintained response plan.
What Is A Breach Plan?
Data breaches can damage the productivity, customer satisfaction and brand of a business. SMEs are often prime targets as they may typically spend less on cyber-security. Onsight cyber-security research found that 42 percent of small businesses have suffered a cyberattack, and this is often attributed to the fact that SMEs are a large target for ransomware as small businesses are less likely to have essential cyber defences and breach detection methods. This makes it even more crucial for these businesses to create and refine a comprehensive data breach response plan.
A data breach response plan helps businesses effectively respond to cyber-security attacks by clearly and extensively laying out steps that aid with managing, and ideally minimising, the damage caused by the breach. These data breach plans should be customised based on the needs and size of your organisation, but this blog post will discuss a few of the key aspects to consider when creating, communicating, and practising your data breach response plan.
Tips to Creating Your Data Breach Plan
1. Maintain a flexible and open approach to your data breach response
It is important to create a breach plan that is flexible and tailored to your company’s needs, as the plan needs to be suitable for any unforeseen incidents. In addition, there needs to be clear communication within the relevant teams to ensure that the response plan is activated quickly and efficiently. IBM found that the average time for a data breach to be identified in 2020 was 228 days, suggesting that once a data breach has been recognised, it is important for all relevant people to be aware and have easy access to the response plan.
Plans should be tested against real-world scenarios and the capabilities of the stakeholders to confirm that the steps are pragmatic and easily understood. It is a recommended practice to do a full end-to-end practice run once a year to ensure familiarity with the steps and processes. This can help achieve a more effective response in case of an actual breach.
Lastly, the plan should be regularly maintained and updated. Frequently assessing new data threats and ensuring that your plan is well adapted to new government legislation concerning data protection is a good way of guaranteeing response flexibility.
By laying out exact internal steps to take after a data breach with the relevant owners of each step, valuable time can be saved and put to better use notifying compromised users, and regulatory authorities. If a breach is suspected based on internal logging, it is best to confirm this and find out if lost data has been made public. Additionally, determining the type of cyber-attack is very important; whether it be theft of data or a ransomware incident, data breach responses will vary significantly.
If the data breach is suspected to be based on an external data dump, then confirming that it is your data, as well as the age of the data, should be the first step. Determining where the breach occurred and disabling compromised user or system accounts in addition to taking the database or storage service offline until the gap can be fixed may be advisable.
It is also important to determine exactly the scope of the data lost, as well as sensitivity levels, and whether users who have been compromised need to be contacted. When deciding the seriousness of a user data breach, the following questions should be considered:
- Are multiple individuals affected by the breach?
- Is there a risk of serious harm to the affected individuals?
- What media or stakeholder attention should be expected due to the data breach?
If it is determined that the breach is serious, it is important to notify relevant authorities and compromised users. Following the breach, it is advised that the response team conduct a post-breach review to assess the effectiveness of the response plan.
While you are creating a breach plan, it can be helpful to consider third-party resources that can support it. For example, the Security Incident Response Guide provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS) works alongside your own operational response plan while being focused on any impacted cloud resources.
2. Use cloud services to aid with data backups after ransomware attacks
Technology, and more specifically, cloud services, can be helpful when planning and responding to data breaches. Services such as AWS Backup and CloudEndure Disaster Recovery enable you to centrally configure backup policies, and monitor backup activity for both cloud and on-premise resources.
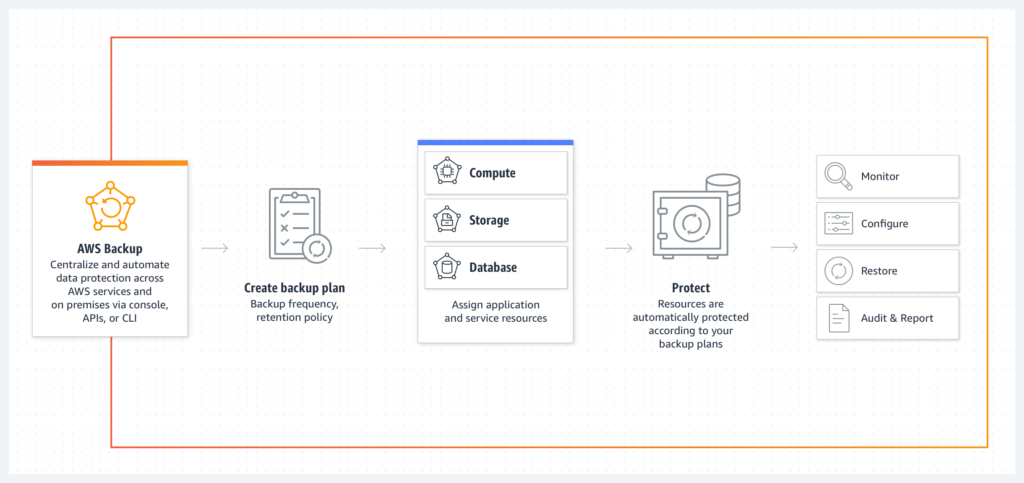
A strong backup and recovery strategy will protect your organisation against the malicious destruction of data and ransomware attacks. Data stored in backups, and suitably protected from attacks, can be easily restored with just a few clicks. Practice is just as critical here as with the data breach plan. Remember the old adage; your backup is only as good as your ability to restore it.
Another service, CloudEndure Disaster Recovery, can return entire servers to the correct versions. Undoing any compromising changes and quickly restoring availability to users after a breach.
The data storage service S3 has versioning, which should be enabled for critical data as this will enable you to easily restore past versions of files in the event of wrongful deletion. Permissions for S3 can be managed at a very fine-grained level. For example, a compromised user account might be able to delete data, but they would not have permission to delete versions. Cross-region replication is another feature of S3, enabling you to create and automatically maintain a backup of your data in a different cloud region.
AWS also provides powerful automation and security services such as GuardDuty, which can automatically detect potential breaches in your cloud environment.
3. Report the data breach to compromised
A data breach response plan should also include a communication plan, which follows all legal notification requirements for notifying parties affected by the breach, including compromised users and employees. Compromised users should be notified of the facts of the data breach and the potential harm that this data breach has caused. As soon as a breach is identified, reporting to a regulator is an important step. However, there is often ambiguity over when exactly to report a detected data breach. If an organisation has credible grounds to believe that a data breach has occurred, it is necessary to report this breach, especially if assessment of the data breach has concluded that it is likely to lead to significant harm to affected users.
If the data breach is serious enough that you have concluded that it affects multiple individuals and their personal data, making a formal announcement as a business is crucial. Users will view such a breach of data the same as a breach of trust and rebuilding that relationship should be a key consideration in how and what you communicate in those early announcements. Using the right wording is very important when drafting a formal announcement. Regardless of the size of your organisation, the announcement should go directly to the individuals affected. For larger organisations, a second announcement to the press is also advisable.
Honesty about data breaches is incredibly important as customers value it. In 2018, Marriott Hotels suffered a data breach that affected around 340 million hotel guests, and the public statement to the press read, “Marriott deeply regrets this incident happened. From the start, we moved quickly to contain the incident and conduct a thorough investigation with the assistance of a leading security expert.” Emails were sent to all affected individuals, which laid out steps to retrieve personal data, and provided a first point of contact for individuals who required more information about the data breach.
While a data breach announcement is never received positively, the public consensus was that Marriott handled it well, with a timely well-worded response and suitable follow-up actions.
Well-handled data breaches are often the ones that are identified with speed, and AWS solutions such as Amazon Detective can aid in analysing potential cyber gaps within your systems.
The timeliness of the communication when announcing a data breach is vital; once the data breach has been confirmed, decisive action needs to be taken to ensure there is no delay in informing compromised users. Equifax took a few months to announce that a data breach had affected 143 million users in 2017. This announcement was released on Twitter, during hurricane season, and with very limited details. Their response website where further details could be found was flagged as a phishing threat and was unreachable in common browsers due to an ill-conceived choice of domain name. There was also public outcry over a legal misunderstanding and insider trading before the breach was announced. All of this resulted in Equifax being widely condemned publicly. Besides the imposed fine, two executives resigned, and a new CEO was appointed.
Clarity, accountability, and transparency are imperative when drafting a formal announcement, and this includes:
- Apologising and explaining the full extent of the data breach
- Providing details on precisely what data has been stolen from affected individuals, and how you are addressing the cause so that it does not happen again
- Sharing clear steps that users can follow to reduce the impact of the stolen data and extending a point of contact to let users know you are there for any concerns they may have
4. Sustain strong logging practice with encryption
Encryption is a key component in protecting data stolen during a breach. Encryption is a common requirement for most privacy and other data regulations, as are implementing robust logging and auditing capabilities – as laid out in more detail in our previous article on privacy.
When a data breach occurs, it should be confirmed if it was taken encrypted or unencrypted. For encrypted data breaches, the security of the encryption keys needs to be verified and locked down as soon as possible. It is best to keep encryption keys and encrypted data in different cloud accounts, as it reduces cyber vulnerability.
Breaches can be analysed in detail by referring to the data access logs stored safely in a separate security account. Where exactly the data was stolen and by which account needs to be identified. Compromised user or system accounts should be blocked, and a root cause analysis performed to understand how the account became compromised. After this, steps should be put in place to prevent the same from happening again.
If consumer data is compromised, strong encryption and logging processes can potentially reduce the regulatory fines that may be issued as a consequence of the breach, as well as help recover some trust between your business and its customers.
Conclusion
Cyberattacks have become the norm for enterprises of all sizes. Accepting that a breach is only a matter of time and preparing accordingly may appear pessimistic, but it is an effective way to reduce the impact of such breaches.
A comprehensive and flexible data breach response plan is the first step in that journey. Breach plans need to be well-communicated amongst relevant teams, actively maintained and practised at least once a year.
As an SME or start-up with a limited budget, the cloud offers several cost-effective strategies in encryption, backups and logging to help reduce the risk of data breaches and to help respond effectively when one does happen. Most importantly, however, after a personal data breach, a strategy that incorporates communication and transparency will be most critical in regaining the trust of compromised customers.
Thomas is a Lead Consultant at Sourced with over 18 years of experience in delivering digital products. He gained a passion for evangelising Serverless architecture through his enthusiasm for cloud and entry into the AWS Ambassador programme.




